Corporate
Governance
Corporate
Governance
What is Corporate Governance?
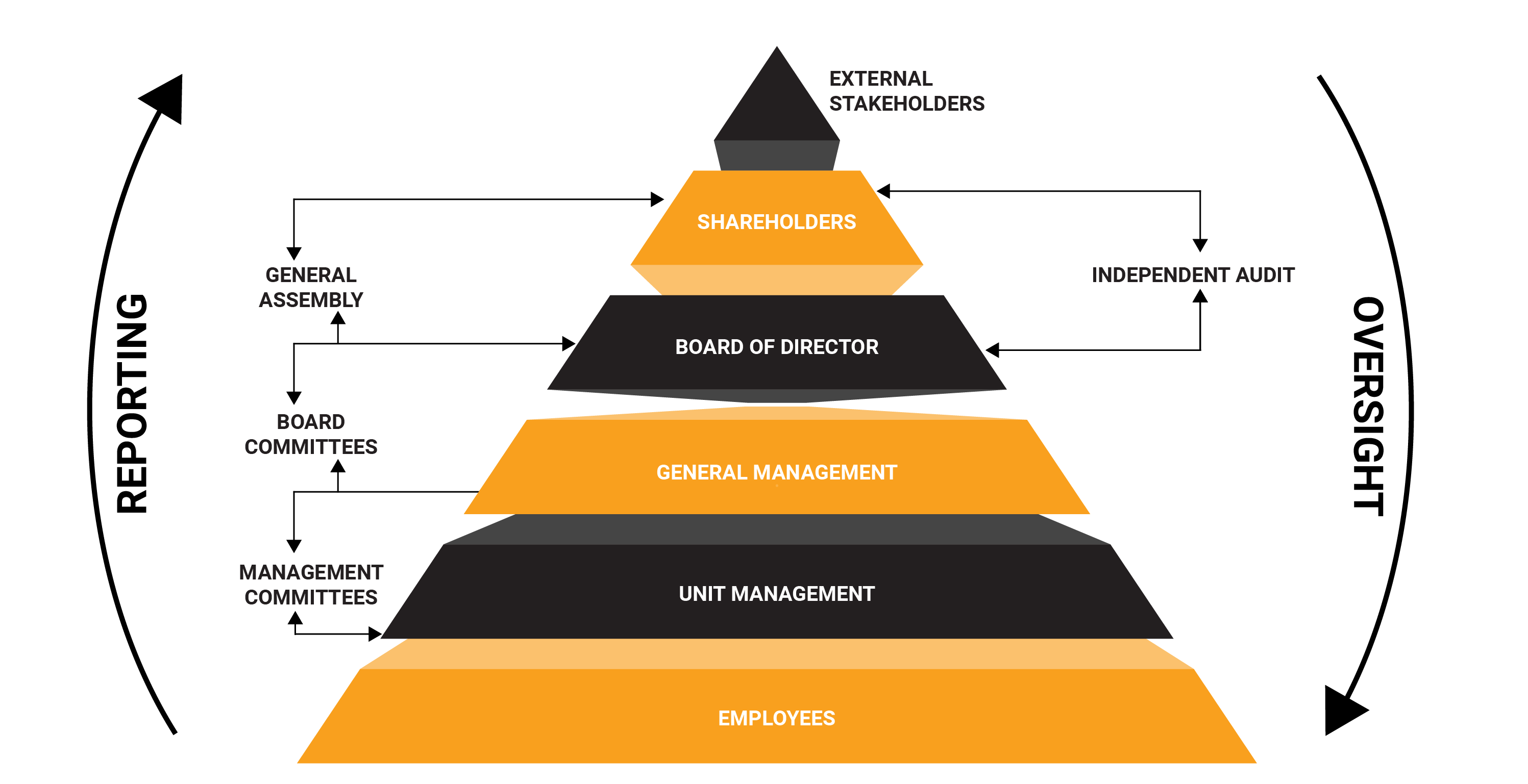
Accountability: How the management of a company is held to account to shareholders and other stakeholders (Accountability = Reporting + Oversight).
Communication: How accountability is communicated to the wider world.
In practice this is:
- The system by which companies are directed and controlled by applying corporate fairness, responsibilities, transparency and accountability
- The mechanism in which shareholders exercise control over management and/or other parties within the company to ensure that all their interests are protected
- It specifies the distribution of rights and responsibilities among different participants in the organization such as the Board of Directors, managers, shareholders and other stakeholders
- It provides the structure through which the organization’s objectives are set and the means of attaining those objectives and monitoring performance
What are Corporate Governance Principles?
In reflection of the OECD’s six principles these are:
- Ensuring the basis of an effective corporate governance framework
- The rights and equitable treatment of shareholders and key ownership functions
- Institutional investors, stock markets, and other intermediaries
- The role of stakeholders in corporate governance
- Disclosure and transparency
- The responsibilities of the board
A. Ensuring the basis of an effective corporate governance framework
The corporate governance framework should promote transparency and efficiency of companies and markets, be consistent with the rule of law and clearly articulate the division of responsibilities within corporations as well as among different supervisory, regulatory and enforcement authorities.
B. The rights and equitable treatment of shareholders and key ownership function
The exercise of shareholders' rights should be protected and facilitated and all shareholders should be treated equitably, including minority and foreign shareholders. All shareholders should have the opportunity to obtain effective redress for violation of their rights.
Basic shareholder rights should include the right to:
- Secure methods of ownership registration;
- Convey or transfer shares;
- Obtain relevant and material information on the corporation on a timely and regular basis;
- Participate and vote in general shareholder meetings;
- Elect and remove members of the board; and
- Share in the profits of the corporation.
C. Institutional investors, stock markets, and other intermediaries
The corporate governance framework should provide sound incentives throughout the investment chain and provide for stock markets to function in a way that contributes to good corporate governance.
- All shareholders of the same series of a class should be treated equally
- Insider trading and abusive self-dealing should be prohibited
- Members of the board and key executives should be required to disclose to the board whether they, directly, indirectly or on behalf of third parties, have a material interest in any transaction or matter directly affecting the corporation.
D. The role of stakeholders in corporate governance
The rights of stakeholders should be recognized and established by law or through mutual agreements and active co-operation between corporations and stakeholders should be encouraged to help in creating wealth, securing jobs, and ensuring sustainability of financially sound enterprises.
E. Disclosure and transparency
Timely and accurate disclosure should be made on all material matters regarding the company, including the financial situation, performance, ownership, and governance of the company.
F. The responsibilities of the board
The Board of Directors is responsible for the strategic guidance of the company, the effective monitoring of management, while the Board itself is accountable to the company and the shareholders.
A cornerstone of these principles is the presence of an effective system of internal controls:
Companies should have an effective independent risk management function, under the direction of a chief risk officer (CRO), with sufficient stature, independence, resources and access to the board.
- Risks should be identified, monitored and controlled on an ongoing company-wide and individual entity basis. The sophistication of the company’s risk management and internal control infrastructure should keep pace with changes to its risk profile, to the external risk landscape and in industry practice.
- An effective risk governance framework requires robust communication within the company about risk, both across the organization and through reporting to the board and senior management.
- The board of directors is responsible for overseeing the management of the company’s compliance risk. The board should establish a compliance function and approve the company’s policies and processes for identifying, assessing, monitoring and reporting and advising on compliance risk.
- The internal audit function should provide independent assurance to the board and should support board and senior management in promoting an effective governance process and the long-term soundness of the company.
All the above should be documented in detail in a company’s corporate governance code.
How Can Ekuiplus Assist?
Ekuiplus can help a business assess the effectiveness of it’s corporate governance framework and identify areas for enhancement and work with companies on implementing the practices and structures to ensure effective corporate governance in their organizations in line with best practice.

